Eggs of fish have long been eaten, and scientist has isolated incredible health benefits that come with eating fish egg. Just like any other food, fish eggs pack beneficial nutrients, including fat and protein.
In this context, masago refers to the roe of capelin. Fish roe is technically fish eggs that have fully ripened. It can be obtained from many varieties of fish, such as salmon, herring, and sturgeon. Capelin is a type of small fish which breeds mostly in the cold waters of the Arctic, North Atlantic, and Pacific oceans. Masago is popularly used in Asian dishes as an ingredient due to its unique taste. This article reviews masago, its nutritional profile, benefits, side effects, and uses of masago.
What Is Masago?
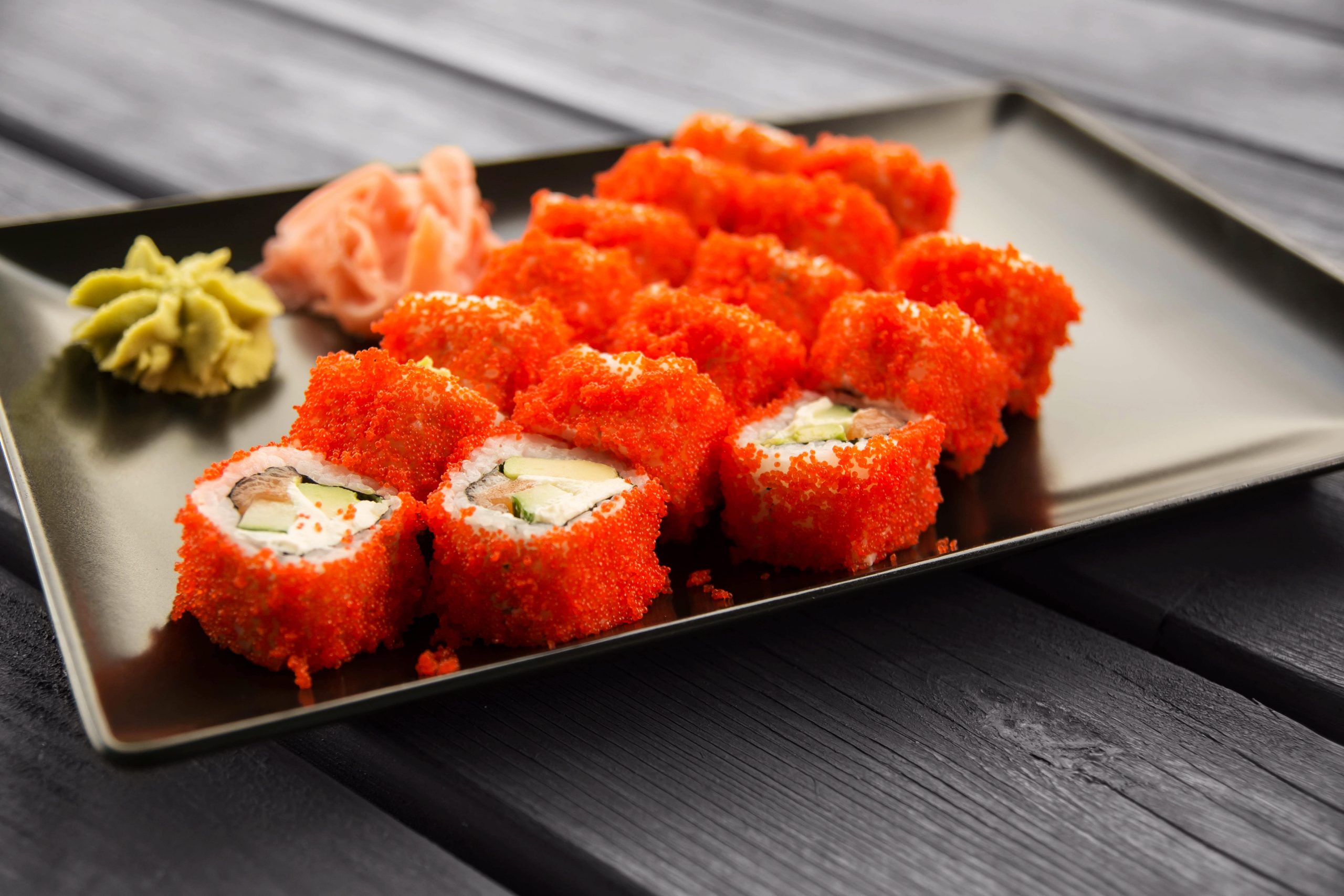
Masago is edible and delicious eggs of the capelin fish, scientifically called Mallotus villosus, and is a member of the smelt family. They are deemed as forage fish since they form a big part of foods eaten by big predators, such as sea birds, whales, codfish, and seal. They have silver-green skin and are small in size, closely taking after sardines. Fishermen do not hunt for capelin just because their flesh is edible but because they want masago and to make other products. According to the National Institutes of Health, up to 80 percent of harvested capelin is utilized for the production of fish oil products and fishmeal. The remaining 20 percent is used to make masago.
Female capelin are considered fully grown by the age of two to four years when it starts to produce eggs, which continues till its death. Before the female capelin starts spawning and is full of eggs, fishermen harvest them to make masago. Masago is a valued ingredient in Asian cuisine and is used as an ingredient in sushi rolls. It has a pale yellow color but cooks sometimes dye it with other hues like red, green, or orange for customer attraction. Its flavor is mild, and in some cases, it can be mixed with ginger, wasabi, or squid ink.
Masago Versus Tobiko – What’s The Difference?
Many people usually confuse Masago with tobiko, which is the eggs or roe obtained from flying fish. It’s true that they may have some similarities, but masago and tobiko have unique differences. Masago is characteristically small and is usually sold at a price less expensive than tobiko. In fact, that is the main reason why many cooks use it in place of tobiko to make sushi rolls. Tobiko has a natural bright red hue, while masago’s hue is sort of pale yellow and is dyed with other bright hues to enhance visual interest. For obvious similarities, masago has the same taste as that of tobiko, with mild crunchy texture. Even with their similarities, sushi rolls are much often completed with masago, because tobiko is deemed expensive and of high quality.
The Nutritional Profile of Masago
Just like other types of fish eggs or roe, masago contains few calories but is loaded with beneficial nutrients. Just 28 g of fish roe provides 40 calories, 2 g of fat, 6 g of protein, less than one gram of carbs, 7 percent of the recommended daily value (RDV) for vitamin, 10 percent of the RDV for vitamin E, 12 percent of the RDV for riboflavin (vitamin B2), 47 percent of the RDV for vitamin B12, 6 percent of the RDV for folate (vitamin B9), 11 percent of the RDV for phosphorus, and 16 percent of the RDV for selenium.
As you can see, fish roe provides high amounts of vitamin B12, which is a water-soluble vitamin. You must aim to get high amounts of this vitamin from your dietary supply because your body is not able to produce it on its own. A deficiency of vitamin B12 makes several critical processes in your body lag behind. It is particularly important for the development of red blood cells, production of energy, transmission of nerve impulses, and synthesis of DNA. Additionally, fish roe is low in carbs but loaded with high-quality protein and heart-friendly fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids.
Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fats, which help your body in several ways. They have anti-inflammatory properties which can reduce your risk of heart disease. Omega-3s also improves the functionality of your immune system, improve heart health, support lung function, and enhance healthy hormonal function. What’s more, fish roe is high in amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. This includes valine, lysine, histidine, isoleucine, leucine, and phenylalanine. Studies indicate that leucine and lysine are important for the repair of torn muscle and synthesis of proteins.
Health Benefits of Masago
Eating the nutritious masago can benefit your health as explained below.
An Excellent Source of High-Quality Protein
Masago’s size should not make you underestimate its nutritional value. A single 28 g of masago provides 6 g of high-quality protein, as much as one large egg can deliver. Protein is effective at managing hunger due to its high satiety property. This is important for weight loss as you will feel full for a long and ultimately consume few calories.
High In Natural Selenium and Vitamin B12
Masago is an excellent source of natural selenium – a vital mineral with antioxidant properties. Selenium is found in seafood in abundance and with its antioxidant properties, reduces cellular damages caused by oxidative stress, supports thyroid health, and boosts your immune system. Vitamin B12 found in masago is important for a healthy nerve function and energy production.
Boasts Herat-Healthy Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s are celebrated for their critical roles in boosting heart health. They are polyunsaturated fats which can reduce inflammation, reduce the risk of heart disease, regulation of blood clotting, and reduced risk of coronary artery disease.
Potential Side Effects
High In Sodium
Cooks often mix Masago with salty ingredients which makes it have high salt content as a final product. Too much consumption of salt increases your risk of blood pressure.
Allergic Reactions
Masago is a seafood product and you need to avoid it if you are allergic to shellfish and fish.
Conclusion
Masago is a fish roe obtained from a mature capelin which resides in the cold waters of the Pacific Ocean. It is used as an ingredient in sushi rolls giving the product a pale yellow or bright red, green, or orange appearance. It is highly nutritious and packs heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Since it is a seafood, you need to avoid it in case you are allergic to fish.
Credits
We would like to thank the below contributors who have helped us to write this article:
- FDC – Giejo Magazine Article - July 29, 2023
- MoriMa Tea the – Chinese tea culture - April 26, 2023
- Missionary Position – Least Likely To Bring You To Climax - April 7, 2023