Blood sugar level is an important factor for a healthy living. The foods you eat play a vital role in keeping it in check. Foods with a high glycemic index can significantly increase blood sugar levels.
Glycemic index is a tool that is often used as a determinant of blood sugar management. The score of a particular food on the glycemic index is influenced by the composition of nutrients, ripeness, method of cooking, and the degree of processing. You can use the glycemic index to choose the kinds of foods you want to eat. It can also help you lose weight, reduce cholesterol, and improve blood sugar control. This article is your eye-opener to everything behind the glycemic index.
What Is Glycemic Index?
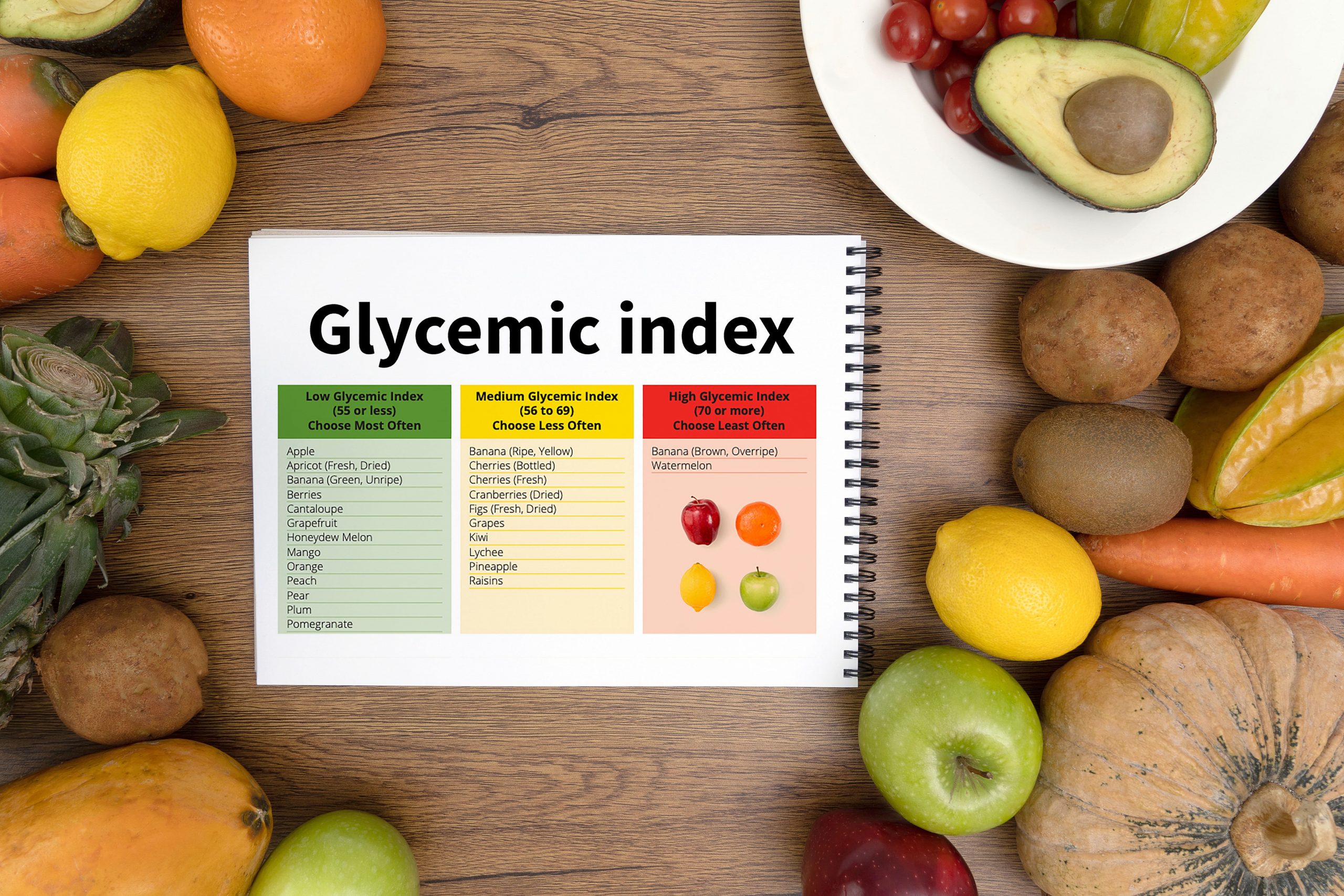
The glycemic index (GI) is a tool used in nutrition to determine how quickly a particular food can raise blood sugar levels. It is a scale that ranks food from 0-100 and classifies them as of low, medium, or high glycemic index. Foods with a low glycemic index are less likely to raise your blood sugar levels. The scale rates foods as follows: high ranges from 70 and above, medium-range from 56-69, while low score 55 or less. Foods containing high amounts of refined sugar and carbs are usually digested quickly and absorbed into the bloodstream and have high GI. Foods loaded with protein, fiber, or fat or often of low GI. Foods without carbs are not rated on the GI and include fish, poultry, meat, herbs, nuts, seeds, oils, and spices. Several factors may also affect the GI of a particular food and include method of cooking, ripeness, degree of processing, and the type of sugar it contains. It worth mentioning that the glycemic index is much different from the glycemic load (GL). The GI doesn’t consider the amount of food eaten when rating foods. The GL, however, considers the number of carbs per serving a particular food has to determine its effects on blood sugar levels. It will, therefore, be of importance to consider both glycemic index and glycemic load as determinants of the type of food you want to eat for healthy blood sugar levels.
Low Glycemic Diet
The low glycemic diet is a form of eating that involves trading foods with high GI for those with low GI.
Benefits
Sticking to low glycemic diet may benefit your health in a number of ways, including:
Improved blood sugar control: Studies have consistently shown that sticking to a low GI diet may lower the levels of blood sugar and improve blood sugar control, especially on people with type 2 diabetes.
Increased weight loss: Some studies have demonstrated that sticking to a low GI diet may promote short-term weight loss. However, more studies should be conducted to determine its effects on long-term weight management.
Reduced cholesterol levels: Following a low GI diet may help reduce your risk of heart disease because it lowers the levels of both total and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) “bad” cholesterol.
How To Follow
To follow the low glycemic diet effectively, you should eat foods that score low on the GI scale such as:
Fruits: lemons, oranges, limes, apples, grapefruit, berries.
Non-starchy vegetables: cauliflower, carrots, broccoli, spinach, tomatoes.
Whole grains: couscous, barley, oats, farro, buckwheat, and quinoa.
Legumes: kidney beans, chickpeas, black beans, lentils.
You can also eat foods that have no rating on the glycemic index to help balance the low glycemic diet, such as:
Meat: pork, lamb, bison, beef.
Seafood: sardines, tuna, anchovies, mackerel, shrimp, salmon
Poultry: turkey, goose, chicken, duck
Oils: avocado oil, coconut oil, olive oil, vegetable oil
Nuts: macadamia nuts, almonds, almonds, pistachios
Seeds: chia seeds, flax seeds, sesame seeds, hemp seeds
Herbs and spices: rosemary, black pepper, cinnamon, dill, basil, turmeric, cumin
The low glycemic diet is relatively free-style, as it has no such restrictions. That being said, you should cut back on your intake of high GI foods. This may include:
Rice: jasmine rice, arborio rice, white rice.
Bread: pit bread, naan, white bread, bagels.
Starchy vegetables: French fries, potatoes, mashed potatoes.
Cereals: instant oats, and any breakfast cereal.
Pasta and noodles: ravioli, lasagna, fettucine, macaroni, and spaghetti.
Sugar-sweetened beverages: sport drinks, fruit juice, soda.
Snacks: microwave popcorn, pretzels, chips, crackers, chocolate.
Baked goods: doughnuts, cookies, croissants, muffins, cakes.
Glycemic Index of Foods
Fruits: Most fruits are of high GI. Watermelon 76, pineapple 59, blueberries 53, mango 51, banana 51, oranges 43, dates 42, strawberries 41, and apples 36.
Vegetables: Boiled potatoes 78, boiled pumpkin 74, boiled sweet potatoes 63, boiled plantains 66, and boiled carrots 39.
Grains: White bread 75, whole wheat bread 74, white rice 73, brown rice 68, popcorn 65, couscous 65, rolled oats 55, quinoa 53, and barley 28.
Legumes: Legumes are considerably low in GI. Lentils 32, chickpeas 28, kidney beans 24, and soybeans 16.
Dairy products: Rice milk 86, ice cream 51, whole milk 39, skim milk 37, and soy milk 34.
Sweeteners: Table sugar 65, honey 61, maple syrup 54, coconut sugar 54, fructose 15.
Effects of Cooking and Ripening on GI
Cooking can significantly affect the glycemic index of some foods. Frying foods for example, makes them contain high amount of fat, which slows down their absorption of sugar thus decreasing the GI. Roasting and baking on the other hand, breaks down resistant starch – which is known to escape digestion and is found in foods like oats, potatoes, and legumes – and increase the GI. Boiling seems to be the best cooking method compared with others, as it preserves the resistant starch and lowers the GI significantly. The longer foods take while cooking such as rice and pasta, simplifies their starch making them more digestible and attain higher GI. Additionally, ripening fruits like bananas reduces their starch content during the process, making them score higher on the GI.
Conclusion
Glycemic index is a tool used to measure how quick one food can raise blood sugar levels. It is affected by factors like ripeness, method of cooking, composition of nutrients, and degree of processing. To follow the low glycemic index, you need to eliminate foods with high GI with those with low GI.
- Learn to Enjoy Self-care Routine - September 21, 2023
- Jonathan Aufray’s Story - July 29, 2023
- From Public Housing To Ivy League: The Inspiring Journey of Crystaltharrell.com and its Founder - June 7, 2023