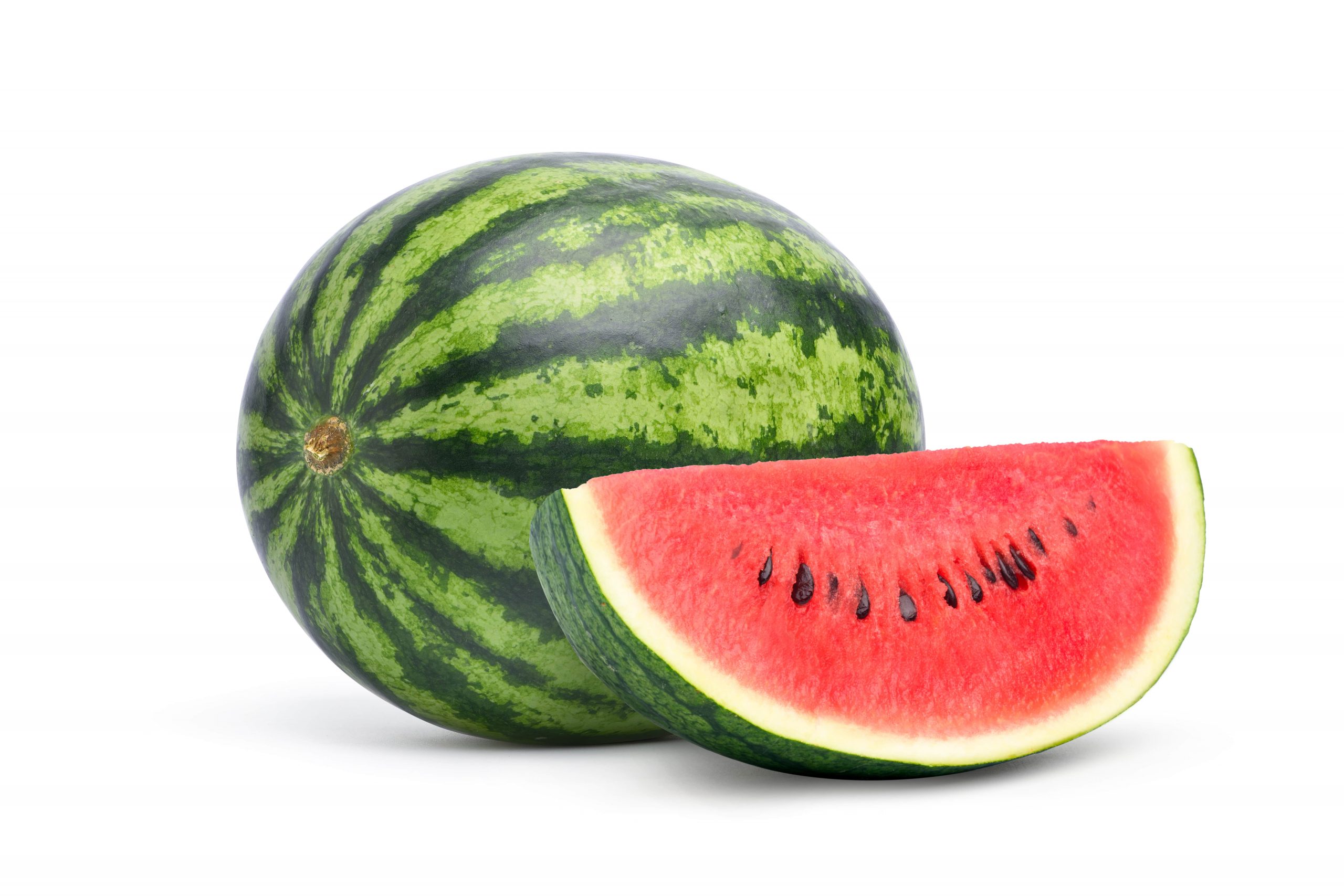
Doctors and health practitioners often recommend watermelon to clients affected by dehydration. This fruit does not only help with hydration but is also rich in nutrients and low in calories.
When nutritionists and dietitians talk about superfoods, watermelon usually comes next after passion fruit. With its origin traced in Southern Africa, watermelon boasts of many nutrients. Besides the nutrients, it is also rich in antioxidants and plant compounds which add to its value. With 91% water content, taking watermelon is so refreshing. You enjoy the water and the nutrients without worrying about putting in extra pounds since it is among the fruits with the fewest calories. Dive into this write-up and learn about the nutritional facts and health benefits of watermelon.
Watermelon: The Nutritional Profile
Just like other foods and dietary elements, understanding the nutritional profile of watermelon will help you appreciate this great fruit with impressive health benefits. 91% of watermelon is made up of water, while 7.5% is made up of carbs. The rest of the percentage (1.5%) comprises fiber, sugar, and very little fat. Weight loss enthusiasts take watermelon as one of the foods for shaking of extra pounds since the fruit has only a few calories and a negligible amount of fats.
i. Carbs
Carbohydrates make up about 7.5% of watermelon content. In a 100g cup serving of watermelon, you reap about 7.5g of carbs. Although small amounts of fiber form part of the carbs in watermelon, the majority comprises simple sugars such as sucrose, fructose, and glucose.Watermelon has a glycemic index of 72-80, meaning that taking it can raise blood sugar levels fast and cause sugar spikes. However, carb content in watermelon is little, making up only 7.5%. This does not put one at great risk of getting sugar spikes.
ii. Fibers
If you are looking for a fruit to remedy your digestive issues or constipation, watermelon is definitely not the fruit of choice. This is because the fruit is low in fiber. Imagine that a whopping 100g serving of watermelon provides only 0.4g fibers! Sucrose is a fermentable short-chain carbohydrate, yet the sugar content in watermelon is primarily sucrose. This usually creates a problem among people with sucrose malabsorption, leading to stomach discomfort.
iii. Vitamin and minerals
Watermelon is also a rich source of vitamins and minerals. For instance, it has copper and potassium, two minerals critical to the body’s functionality. The body needs potassium to balance osmotic pressure, maintain blood pressure, and the good condition of the heart. Watermelon is also packed with vitamin A, vitamin B5, and vitamin C. Vitamin A is good for eyesight, while vitamin C strengthens the body’s immune system, fights oxidative stress and inflammation, and reduces one’s risking of contracting illnesses.
Watermelon: Plant Compounds
Besides the nutrients discussed in the preceding section, watermelon is also rich in antioxidants and plant compounds that the body needs. Two of them are citrulline and lycopene.
i. Citrulline
Of all the dietary sources of antioxidant citrulline, watermelon tops the list. Its white film covering the flesh harbors the highest amount of citrulline, which is immediately converted to arginine once in the stomach. Arginine is a form of essential amino acid. The reason nutritionists value watermelon is because the citrulline it has alongside arginine ensures there is enough dilation, ultimately monitoring the blood pressure.
Arginine has multiple uses. Some studies claim that it can help wounds heal faster. The immune system and various organs such as the lungs and kidney also depend on arginine for their functionality. One factor worth noting is that watermelon is both a dietary and blood source of arginine and citrulline. This means that as you take it, you are boosting your arginine and citrulline levels in the body.
ii. Lycopene
Fresh tomatoes and the inner part of fresh watermelon have one thing in common; they are both rich in lycopene. It is the presence of lycopene plant compound that makes watermelon and tomato red. The body uses the lycopene to make beta-carotene, which is then converted to vitamin A for vision.
Health benefits of watermelon
Studies name watermelon among the fruits with many health benefits. Here are the health benefits that you can reap from eating a piece of watermelon;
i. It May help lower blood pressure
High blood pressure increases a person’s risk of suffering from heart disease and other lifestyle diseases, which is why any food that helps reduce such a risk is appreciated. As mentioned previously, watermelon is rich in citrulline, an antioxidant that’s converted to arginine once in the body. The body needs citrulline and arginine to make nitric acid, a gaseous compound that keeps the blood vessels dilated and eases them of pressure.
ii. May help in managing sore muscles
When many people take part in strenuous exercises, the muscles get sores. Watermelon comes in handy to help with muscle soreness. Its unique nutritional profile enables it to relax muscles. Although studies on this claim are mixed, with some saying that watermelon does not really help strained muscles, the majority of studies (mostly observational) show that watermelon could actually help relax strained muscles.
iii. It May help reduce insulin resistance
Many people who have metabolic syndrome or diabetes type 2 suffer from insulin resistance. This describes a condition in which the human body does not respond to insulin production. When this happens, the affected person’s blood pressure may rise, going even beyond the normal. Yet, high blood pressure is linked to many lifestyle diseases, heart disease included.
Watermelon allergy
The sweet watermelon fruit is a good fruit. Many people eat the fruit and enjoy it without fearing for any allergy. However, a few people can suffer from watermelon’s oral allergy. This kind of allergy affects the lips, mouth, and throat, among other body parts. The parts usually swell and taste itch.
Conclusion
Watermelon is a sweet fruit with many health benefits. The fruit is rich in nutrients and antioxidants, all of which are critical to the body. This article has shared all you need about watermelon. Dive into it to understand the nutritional profile of watermelon as long as other pieces of information.
- FDC – Giejo Magazine Article - July 29, 2023
- MoriMa Tea the – Chinese tea culture - April 26, 2023
- Missionary Position – Least Likely To Bring You To Climax - April 7, 2023