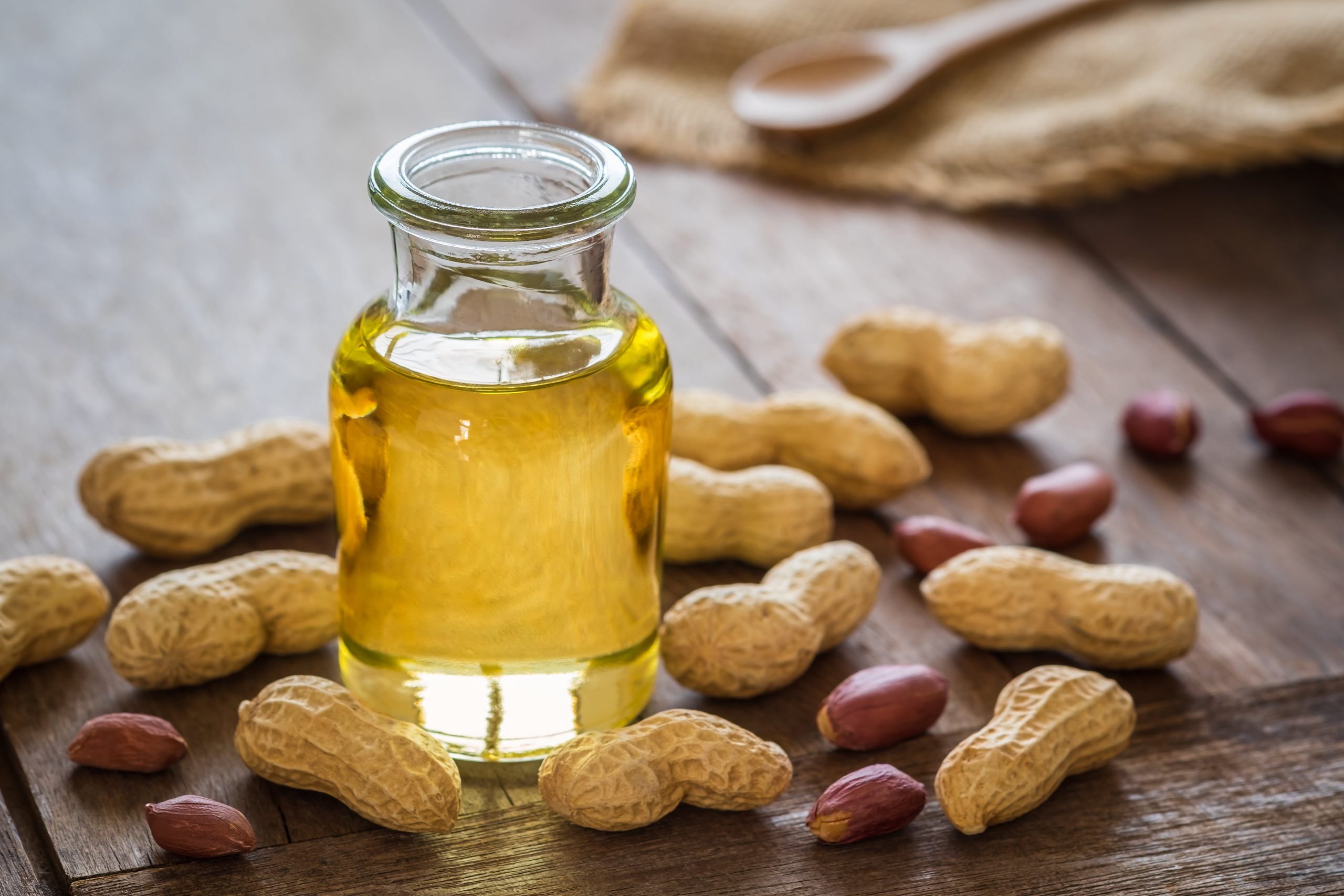
Although peanut oil is a popular vegetable oil because of the many advantages it might have, knowing its drawbacks helps you know whether or not it would make your healthy choice.
The vegetable oil industry offers us multiple choices to choose from, and peanut oil is one of them. The oil is extracted from peanut leaves which can be processed using several different methods. It has multiple advantages, including increased insulin sensitivity and reduced heart disease risks. However, the saturated fat concentration in the oil is a concern, making it pro-inflammatory. Read this article to understand more about types of peanut oils, their benefits, and the health implications of consuming the oils.
Understanding peanut oil
Before getting to the details about peanut oil’s potential benefits and health risks, we need to first understand what it is. Peanut oil is a type of vegetable oil extracted from the leaves of peanut plants and is often called arachis or groundnut oil. Groundnut is used as an alternative for peanuts because as the flowers proliferate above the ground, the nuts grow and mature underground. Peanut oils feature different flavors like other vegetable oils, including sweet and mild, or nutty and strong.
Types of peanut oil
Although all the companies that manufacture peanut oils use peanut leaves, the processing techniques are different, resulting in the different types of peanut oils, including;
- Peanut oil blends made by mixing peanut and other similar-tasting but cheaper oils, including soybean oils, and are widely used for frying food.
- Refined peanut oils undergo refining, bleaching, and deodorization to eliminate the allergenic parts, making them ideal for peanut-allergic people. If you eat fries and chicken from restaurants and first foods, you likely consumer refine peanut oils often.
- Gourmet peanut oil is a great choice for stir-fries, primarily because of the roasting process that enhances the oil’s strong, intense, and deep nutty flavor, ideal for the dishes for which it is used.
- Cold-pressed peanut oils are produced by subjecting peanut leaves to a low-heat process that forces oil out of the leaves while retaining nutrients and the natural flavors in the oil.
Peanut oils- nutritional breakdown
In gauging the health benefits of any dietary component, nutritionists and health experts rely heavily on their nutritional breakdowns. Peanut oils do not fail us either because they are rich in specific nutrients. On average, a tablespoon of peanut oil contains 27.9 mg phytosterols, 11% RDA vitamin E, 119 calories, and 14 g of fats. The oil also contains saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats at 20% (2.3 g), 50% (6.2 g), and 30% (4.2 g) proportions. The fat content majorly consists of palmitic acid (saturated fats), linoleic acid (omega- 6 fatty acid), and high amounts of monosaturated oleic acid (omega 9).
Peanut oils are ideal for frying because of the moderate amounts of monounsaturated fats found in them, which is why they are commonly used for frying in restaurants. However, they only have small amounts of polyunsaturated fats, making them unstable at room temperature. Omega- 6 fatty acids may have few health advantages but are pro-inflammation and linked to many health problems. However, we must mention that the vitamin E in the peanut oils provides an added advantage since it enhances the oils’ antioxidant properties and lowers heart disease risk.
Potential health benefits of peanut oils
Peanut oils have been associated with the following health benefits;
Rich in vitamin E
One tablespoon of peanut oil constitutes 11% of the RDA vitamin E, a ground of compounds with multiple functions, including protecting the body from free radical damage. If the free radicals are left unattended, they accumulate and cause oxidative stress, ultimately increasing the risks of many diseases and weakening the immune system. Vitamin E also helps with cell signaling, the formation of red blood cells, and enhanced blood clotting.
May lower heart disease risk
Heart disease is among the global top-killer diseases and includes many conditions affecting the circulatory systems. While studies are still mixed about the effects of saturated fats on heart disease risk, there is enough evidence that replacing them with mono and polyunsaturated fats reduces the chances of contracting heart problems. Peanut oils have moderate amounts of the two fats and may help trim down bad cholesterols and triglycerides linked to increased heart disease risk.
May help in blood sugar control
Several studies have shown that polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats (all of which are found in peanut oils) can significantly help improve blood sugar control. For instance, these fats resulted in increased insulin secretion and sensitivity in the study subjects. When more insulin is produced and sensed by cells, more glucose is absorbed, reducing blood sugar levels, which translates to reduced chances of diabetes type 2 and better control for the disease for diabetic individuals.
Potential risks of peanut oils
Peanut oils promise several health benefits, but they do not come without health risks, including;
High amounts of omega- 6 fatty acids
Omega- 6 fats are essential fats that must be obtained from diet. The body needs them for good brain development, but too much of the fats leads to increased risks of inflammation. In fact, following the tremendous increase of this fat in modern diets, obesity, cancer, diabetes type 2, inflammatory bowel syndrome, and other inflammation-related diseases have risen.
High chances of oxidation
Oxidation denotes how a substance reacts with oxygen to produce free radicals, the dangerous compounds that accumulate to cause oxidative stress and increase the risk of chronic diseases. Peanut oils are rich in polyunsaturated fats that are more prone to oxidation. In fact, the slightest exposure of the oils to moisture or sunlight induces oxidation, releasing the dangerous compounds in the surroundings and food.
Increased risks of cancer, eyesight loss, and premature aging
Using peanut oil regularly subjects one to free radical interaction whenever the unsaturated particles oxidize. The more free radicals released, the higher the chances of suffering from cancer and going into premature aging.
Conclusion
Peanut oil is made from peanut leaves through crushing, low-heat subjection, or roasting. Although it is praised for its smoke point and vitamin E concentration, its effects are more far-reaching. The risk of oxidation and the high concentration of omega- 6 fatty acids are the major concerns, and both are linked to increased risks of chronic conditions. Therefore, switching to less risky options like extra virgin coconut, olive, or avocado oil would be the best way to go.